By Patrick O’Hara & Ed Baker, LGPS Central
Do words matter? In the wake of COP 28, this has been the question that many in the climate and energy space have been asking. The annual UN climate talks managed to get 200 countries to agree to “transitioning away from fossil fuels in the energy system”, which was a significant improvement on agreements in previous years where government representatives had agreed to “phase out unabated coal and inefficient fossil fuel subsidies”.
Whilst a win for COP insiders – will this matter for financial markets?
The realisation of tangible outcomes from this agreement hinges upon governments following through with their commitments. In the immediate aftermath of COP28, the UK government pledged £1.5bn in extra funding for energy efficiency measures and heat pumps, as well as confirming that the UK will introduce a carbon border adjustment mechanism1. Whilst the EU has initiated discussions of 2040 targets, Japan, a large coal consumer, announced at COP that it will phase out coal power, with China confirming in the UEA that it will update its climate targets by the end of 2025 as part of the second ratchet2 of the Paris Agreement. Below, you’ll find a condensed overview, highlighting the key advantages and drawbacks arising from COP 28.
Unsung stories of COP 28 (& 2023)
For all the focus on language and fossil fuel supply, some developments went under the radar in 2023 and COP, the latter often used as a platform for announcements.
- The dramatic rise of solar production capacity in 2023. To the surprise of many energy analysts, global solar production capacity saw a 1.7x increase (see Rystad chart below) in the past 12 months. Putting the production of a key clean energy on track, for now, with a 1.5 °C aligned pathway.
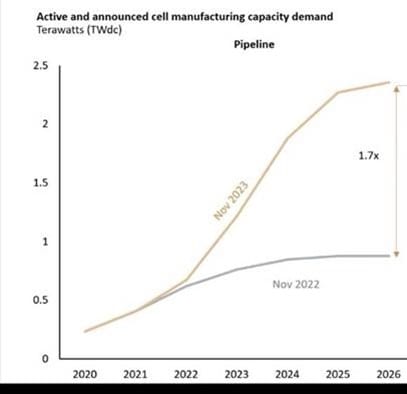
Source: Rystad
- The UAE goes on a $200bn (mostly) green infra investment spree (FT). Recently announced deals include 49% stakes in UK offshore wind farms and an increased equity investment in a Chinese EV company.
- Singapore’s traffic light taxonomy. The Monetary Authority of Singapore became the first government to publish a red, amber and green taxonomy. The taxonomy assigned sector level thresholds, which tighten over time, to activities which are aligning with the Paris Agreement (green), transitioning towards green (amber) and those that are not eligible (red). This could influence regional developments along with those in the UK, Australia and Canada. This is expected to have applications in investment screening, reporting and also financial product design.
- Climate trace. Arguably taking the prize for the coolest climate tech at COP was Climate Trace, an Al Gore-backed non-profit, which utilises satellite remote sensing to provide an open-source database and visualisation of emissions from 352 million assets. This type of asset-level data could potentially mean investors would not in future need to rely only on company reports for emissions data. While information on physical asset data has been accessible for a while, this endeavour is likely to expedite its progress.
Outlook for 2024
Two billion people will go to the polls this year. The outcomes, not least the fork-in-the-road election in America, will matter for climate change. Yet, the momentum behind the transition is also market-driven with trillions of dollars of investment needed annually particularly in heavy emitting sectors and in emerging and developing markets. The fast rate of change in the power and automotive sectors (the post-September slowdown in the UK has not been globally significant, worldwide EV sales grew by 35% in 2023 according to the IEA) are set to continue and this has the greatest potential to reduce emissions in line with countries’ 2030 climate goals.
LGPS Central will continue to track these developments, as well as in partnership with external managers, seek opportunities for meaningful corporate engagement and public advocacy consistent with our net-zero commitments.
Assessing COP 28
| Positive Progress | More To Do |
|---|---|
| Governments Agreement to “transition away from fossil fuels in the energy system”. Agreement to triple renewable capacity & doubling energy efficiency improvements by 2030. Agreement to “substantially” reduce methane emissions by 2030. The UAE hosts have, over the past year invested $200bn, mostly in green infrastructure. Framework and initial funding agreed for a “loss and damage” fund. 25 countries including the U.S. and China pledging to triple nuclear capacity by 2050. Industry Oil & gas decarbonisation charter. 50 of the largest oil & gas companies agreeing to cut operational emissions, stop routine gas flaring by 2030 & eliminate methane leaks. Numerous other announcements & initiatives (examples of these were noted in the “unsung stories” section) | Governments Incremental progress when a breakthrough is needed for 1.5 °C. Loopholes in the summit agreement to allow for “transition fuels”. Financial support for developing countries. Still short at $83bn in 2022 of the $100bn per year that was promised. Moreover, Oxfam has highlighted that approx. $60bn of what is provided is in interest-bearing loans and therefore “not real financial support”. This aspect of the talks continues to be hotly disputed. Industry Oil & gas decarbonisation charter. Lack of commitments on scope 3 emissions. Record number of those with general interest, rather than policy makers in attendance. Over 85,000 attended COP 28.A 70% increase on last year & 50,000 more than attended in Paris in 2015. |
End notes
1 The carbon border adjustment mechanism is a policy tool which puts a carbon price on carbon-intensive raw materials (or goods) being imported into a country. The mechanism already exists in California and will be introduced in the EU in 2026. The purpose is to incentivise countries that don’t have carbon pricing policies to put a pricing scheme, or comparable policy mechanisms, in place.
2 second rachet. This refers to the structure of the Paris Agreement, which is designed so that countries update and tighten their climate commitments and policies every five years.









